Quick facts about cultural similarities between Estonia and other nordic countries.
- Estonians are Finnic people (like Finns and Saami people – both considered Nordic today) and the language is a Finnic language. Latvians and Lithuanians are Balts who speak Baltic languages.
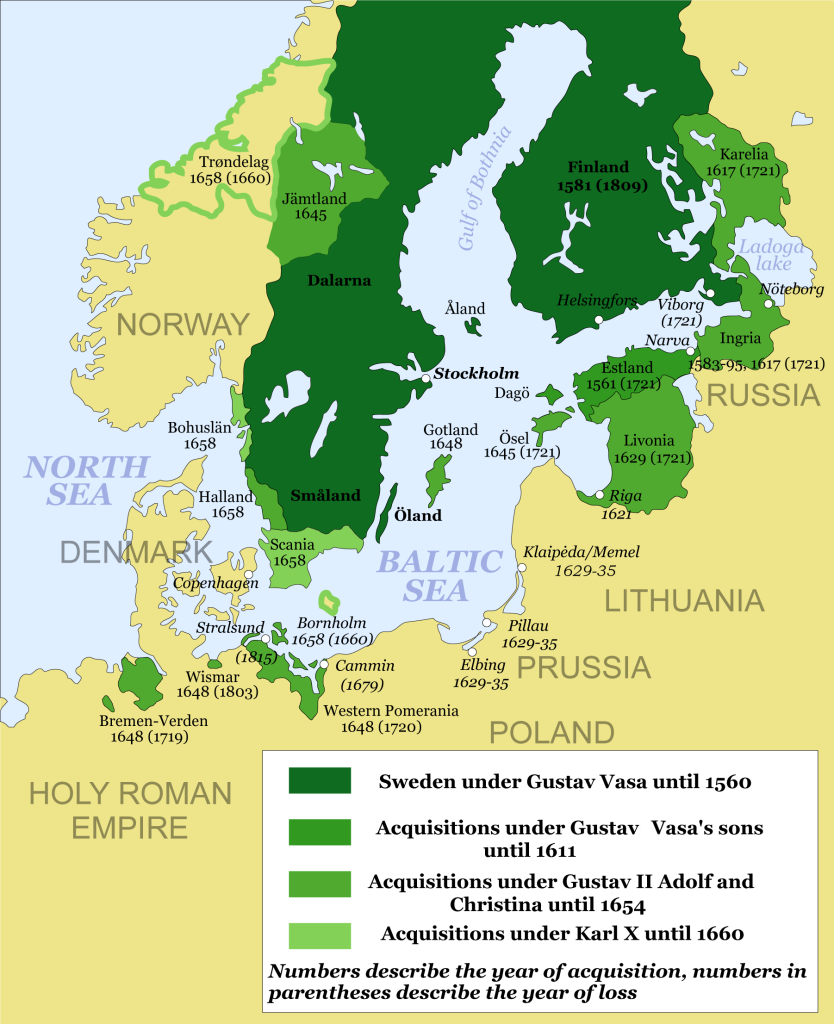
- Estonia used to be part of both Denmark (firstly during the 13th–14th centuries (1219 – 1346) and again in the 16th–17th centuries (1559 – 1645) and Sweden (from 1558 to 1710). A total of 279 years under Scandinavian rule, more than Russian Empire and Soviet occupation combined.
- Swedish time is even today, after 400 years, remembered as ‘the good old Swedish times‘ (hea vana Rootsi aeg).
- Sweden’s
4th2nd oldest university from 1632 is located in Estonia, the Tartu University. Gustav Adolf II set up multiple schools and re-organized the societal and administrational structures such that they left a big impact.
- Tallinn, the capital of Estonia probably got its name from taani linn, literally “Danish city”.
- Estonia’s Coat of Arms is derived from the Coat of Arms of Denmark, dating from 13th century.
- Danish flag, the Dannebrog originates from Estonia according to the legend, in 1219. All Nordic cross flags are derived this flag. There are many Nordic cross flags used for county flags in Estonia, dating back to 13th century.
- 15% of the words in Estonian language are loans from Germanic origin (because German was the language of the cultural and political elite since 12th century right up till 1919). Many word loans have also come from Swedish, Old Norse, Baltic-German, Russian, Old-Russian, Finnish and Baltic languages.
- Estonians are included in the Old Norse Icelandic Sagas as Víkingr frá Esthland (Vikings from Estonia). Estlanders fought along the side of Swedes against the Danes in the Battle of Bråvalla. Saaremaa (Ösel) has the richest finds of Viking treasures after Gotland in Sweden and often raided both Christians and Pagans, in their ships that had a high prow shaped like a dragon or a snakehead as well as a quadrangular sail.
- Estonia had Swedish minorities living here peacefully in cooperation for 8 centuries (until WW2), they were offered cultural autonomy and self-governance in 1925, something that was exceptional in Europe at the time and earned a great deal of international acclaim, the local Swedes thanked and declined, showing they were okay with how things were. Some islands still have dual language shop and street signs. Estonia’s main largest islands are still named Ösel and Dagö in Swedish.
- Estonians call themselves põhjamaalased (“northern people”, another translation would be literally “nordic people” as põhjala is often translated as nordic), it’s such in many folk songs that are almost equal in importance to the national anthem.
- The familiar Swedish red paint color is also common in Estonia. Especially so on the islands.
- Estonians are historically Protestant Lutherans. Lithuanians are Catholic and Latvians are a mix in-between.
- Estonians used to use the Runic calendars (like everybody else in the Northern Europe). Sirvikalender in Estonian.
- Estonians strongly celebrate the Midsummer Day.
- Estonians eat vastlakukkel/semla.
- Estonians drink mulled wine on Yule time (Christmas).
- Estonians like to cross-country ski
- Estonians go to sauna a lot